Perfect Tips About What Is The 3% Voltage Drop Rule

10b Total Resistance And Voltage Drop Principles YouTube
Understanding the 3% Voltage Drop Rule
1. What's the Big Deal with Voltage Drop?
Okay, let's talk electricity. Imagine your electrical system as a highway system for electrons. Voltage is like the pressure pushing those electrons along. Now, as those electrons travel through wires — especially over longer distances — they encounter resistance. Think of it like potholes on that electron highway. This resistance causes a loss of voltage, also known as voltage drop. Too much voltage drop, and your appliances might start to grumble, flicker, or even refuse to work properly. That's where the 3% voltage drop rule comes in; it's the electrical equivalent of keeping those potholes to a minimum.
The core idea behind the 3% voltage drop rule is to ensure that your electrical devices receive enough voltage to operate efficiently and safely. If the voltage drops too low, motors can overheat, lights can dim, and sensitive electronics can malfunction. It's like trying to run your car on fumes — it might sputter along for a bit, but eventually, it's going to leave you stranded. So, maintaining a healthy voltage level is crucial for the overall performance and longevity of your electrical system. It prevents unnecessary strain and ensures that everything runs smoothly. Think of it as preventative medicine for your electrical appliances.
Now, why 3%? Well, electrical engineers, in their infinite wisdom, have determined that a voltage drop of more than 3% can start to cause noticeable problems with most electrical equipment. It's a generally accepted threshold that balances performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. It's not a hard and fast law carved in stone, but it's a guideline that helps ensure that your electrical system remains in good working order. Think of it as a speed limit — you can go a little over, but pushing it too far could lead to trouble.
In essence, the 3% voltage drop rule acts as a safety net, preventing voltage from dipping to levels that could negatively impact your electrical devices. By adhering to this rule, you're essentially guaranteeing that your appliances and equipment are receiving the proper "fuel" to operate optimally. Its a simple yet essential principle that contributes to a stable and reliable electrical system.

Ohm's Law Voltage Drop Calculator
Delving Deeper
2. The Math Behind the Magic
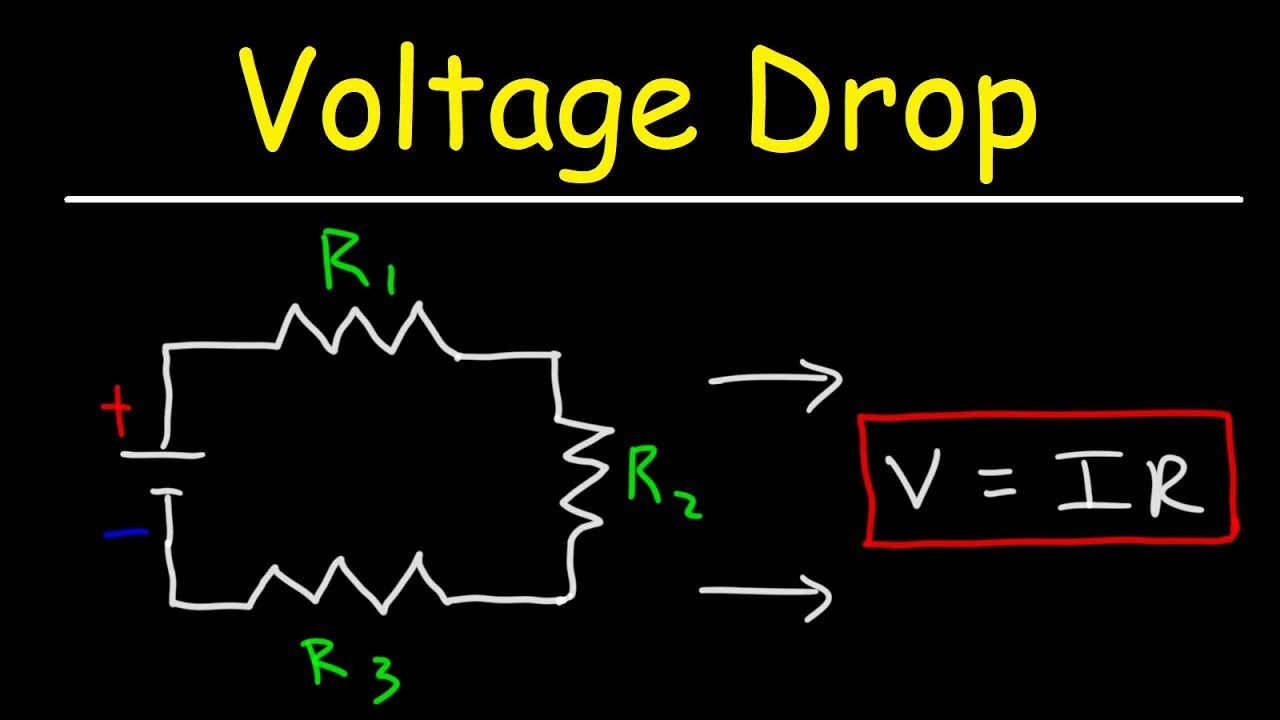
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty (okay, maybe not that nitty-gritty). Calculating voltage drop isn't as scary as it sounds. The basic formula involves a few key factors: the length of the wire, the current flowing through it (amps), the wire's resistance per unit length, and the voltage at the source. Now, I won't bore you with a bunch of equations, but essentially, you're figuring out how much voltage is "lost" as the current travels through the wire. There are plenty of online calculators that can do this for you, so you don't have to dust off your old physics textbook.
The calculation's accuracy depends on having the right inputs. Knowing the exact length of the wire run is critical — underestimate it, and your calculations will be off. Similarly, you need to know the actual current draw of the circuit, not just the breaker size. And, of course, using the correct resistance value for the wire gauge and material is paramount. Getting these details right ensures that your voltage drop estimate is as accurate as possible. Think of it like baking a cake — get the measurements wrong, and you'll end up with a flat, sad dessert.
In addition to the basic formula, remember to account for any additional factors that could contribute to voltage drop. For instance, if you're using multiple conductors in parallel, the calculation will be different. Similarly, if you're dealing with AC circuits, you'll need to consider impedance instead of just resistance. It's a bit more complex, but understanding these nuances is essential for accurate voltage drop calculations. Consult an electrician if you are unsure.
Keep in mind that temperature can also affect a wire's resistance, and thus, the voltage drop. Hotter wires have a higher resistance, so in situations where wires are likely to get hot, its wise to factor this in. It can be useful to consult temperature correction tables or use online calculators designed for this purpose. Taking these additional factors into account helps ensure that your calculations are realistic and reflect real-world conditions.
Why is the 3% Voltage Drop Rule Important?
3. Protecting Your Investment, One Electron at a Time
So, why bother with all this voltage drop stuff? Well, for starters, excessive voltage drop can damage your equipment. Motors, for example, draw more current when the voltage is low, which can lead to overheating and premature failure. Similarly, electronic devices can malfunction or even become damaged by unstable voltage. It's like feeding your car the wrong kind of fuel — it might run for a while, but eventually, it's going to cause some serious problems.
Beyond equipment damage, excessive voltage drop can also impact the performance of your electrical system. Lights may dim, appliances may run sluggishly, and sensitive electronics may behave erratically. It's like trying to run a marathon with a flat tire — you might be able to finish, but you're not going to perform at your best. Maintaining a healthy voltage level ensures that your electrical system operates efficiently and reliably.
Moreover, complying with the 3% voltage drop rule is often a code requirement. Electrical codes are designed to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations, and they often incorporate voltage drop limitations. Ignoring these codes can lead to failed inspections, fines, and even safety hazards. Adhering to the 3% rule not only protects your equipment and ensures optimal performance, but it also keeps you on the right side of the law.
In summary, the 3% voltage drop rule isn't just some arbitrary guideline — it's a fundamental principle that protects your investment in electrical equipment, ensures optimal performance, and keeps your electrical system safe and compliant. By understanding and adhering to this rule, you're essentially safeguarding your electrical infrastructure and preventing costly problems down the road. It's a small price to pay for peace of mind and long-term reliability.
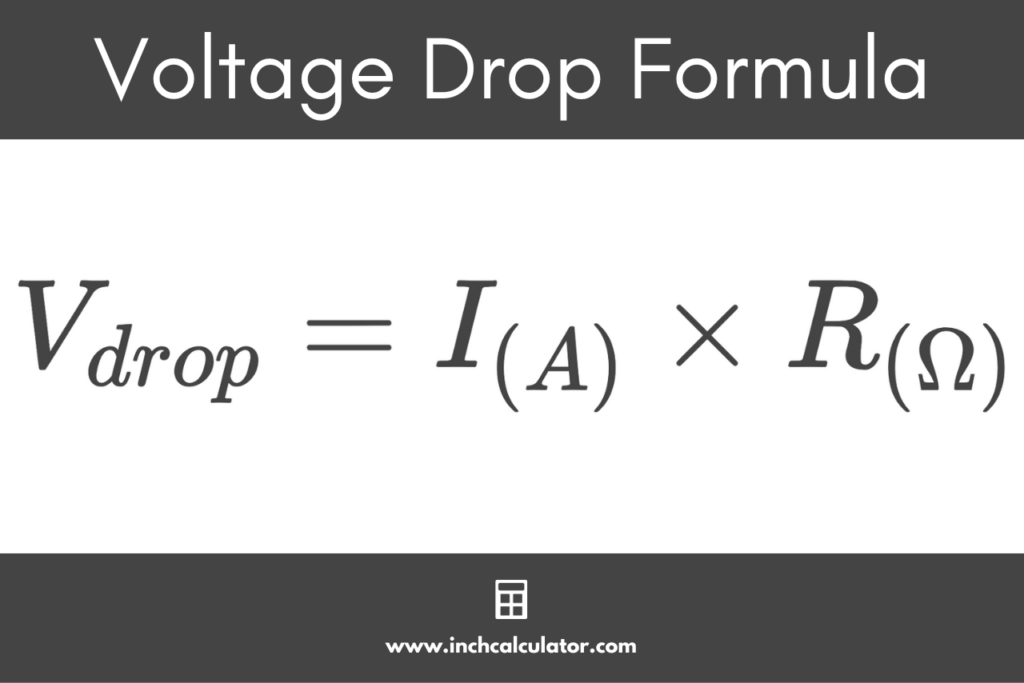
How To Calculate Voltage Drop Across Each Resistor At Diana Massey Blog
Practical Applications
4. From Homes to Factories
The 3% voltage drop rule is particularly important in situations where you have long wire runs, high current loads, or sensitive electronic equipment. Think about a workshop with power tools located far from the electrical panel, or a home theater with expensive audio-visual equipment. In these cases, voltage drop can have a significant impact on performance and reliability. That remote shed you are wiring for power? 3% voltage drop is your new best friend.
In residential settings, the 3% rule is especially critical for circuits that supply power to refrigerators, air conditioners, and other high-demand appliances. These devices require a stable voltage supply to operate efficiently, and excessive voltage drop can lead to premature failure. It's also important to consider voltage drop when wiring outdoor lighting or landscaping equipment, as these circuits often involve long wire runs.
In commercial and industrial settings, voltage drop can have even more significant consequences. Motors, pumps, and other heavy machinery are particularly sensitive to voltage fluctuations, and excessive voltage drop can lead to reduced productivity, increased energy consumption, and even equipment damage. It's also important to consider voltage drop when wiring data centers or other facilities with sensitive electronic equipment, as these devices require a stable and reliable power supply to function correctly.
Ultimately, the 3% voltage drop rule applies to any electrical circuit where performance, safety, and reliability are paramount. Whether you're wiring a small home office or a large industrial facility, understanding and adhering to this rule is essential for ensuring the long-term health and efficiency of your electrical system. It's a foundational principle that helps to prevent problems before they even arise, ensuring that your electrical infrastructure remains in tip-top shape for years to come.

Diodes Constant Voltage Drop YouTube
How to Minimize Voltage Drop
5. Keeping the Flow Strong
So, how do you actually minimize voltage drop in your electrical system? One of the simplest and most effective methods is to use larger wire gauges. Thicker wires have lower resistance, which means less voltage drop over a given distance. It's like widening the pipes in your plumbing system — more water can flow through with less pressure loss. This might seem obvious, but it is often overlooked.
Another way to minimize voltage drop is to shorten the length of the wire run. The shorter the distance the current has to travel, the less voltage drop it will experience. If possible, locate electrical panels closer to the load or use multiple panels to distribute the load more evenly. Its all about finding the right balance between cost, convenience, and electrical performance.
Using higher voltage circuits can also help reduce voltage drop. For example, switching from a 120-volt circuit to a 240-volt circuit can significantly reduce the current required to deliver the same amount of power, which in turn reduces voltage drop. This is a common technique used in commercial and industrial settings. But remember, it's crucial to choose the correct voltage for your devices and appliances.
Finally, make sure all your electrical connections are clean and tight. Loose or corroded connections can add resistance to the circuit, increasing voltage drop. Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical connections to ensure that they are in good condition. Think of it as giving your electrical system a regular tune-up — it'll run more smoothly and efficiently.

How To Calculate Voltage Drop In A Dc Circuit » Wiring Draw And Schematic
FAQs About the 3% Voltage Drop Rule
6. Your Questions Answered
Q: What happens if I exceed the 3% voltage drop limit?
A: Exceeding the 3% limit can lead to various problems, including reduced equipment performance, overheating, premature equipment failure, and even safety hazards. Lights may dim, motors may run sluggishly, and electronic devices may malfunction. It's best to stay within the limit to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Q: Does the 3% rule apply to all circuits?
A: While the 3% rule is a good guideline for most circuits, there may be exceptions. For example, some circuits may have specific voltage drop requirements based on the type of equipment they serve. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications and local electrical codes to determine the appropriate voltage drop limits for your application.
Q: Can I use an online calculator to determine voltage drop?
A: Yes, online voltage drop calculators can be a helpful tool, but be sure to input accurate information, including wire length, current draw, and wire gauge. Keep in mind that these calculators provide estimates, and it's always a good idea to verify the results with a qualified electrician, especially for critical applications.
Q: Is the 3% voltage drop rule a legal requirement?
A: The 3% voltage drop recommendation is often incorporated into electrical codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC). While not always a strict legal requirement, adhering to these codes is generally necessary for compliance and safety. Failing to meet code requirements can result in failed inspections and potential liabilities.