First Class Info About Is WiFi 7 Faster Than Ethernet

The Great Speed Debate
Let's dive straight into the question that's probably got you here: Is WiFi 7 really faster than Ethernet? It's a bit like asking if a race car is always faster than a train — the answer, as usual, is "it depends." We're going to unravel this tech tangle and see where each technology truly shines. We'll break down the theoretical speeds, the practical speeds you might actually experience, and a few things that can throw a wrench in the works. Think of it as a friendly chat about all things network-y.
Now, before we even get started, lets acknowledge that tech moves fast. Whats cutting-edge today could be old news tomorrow (though Ethernet has been stubbornly reliable for, well, ages). We're talking about current technologies as of right now, so keep in mind that these things are subject to change!
Imagine you're trying to download the latest season of your favorite show. Do you want it to load in seconds, or do you have time to make a sandwich (or two) while you wait? Thats what this all boils down to, doesnt it? It's about getting things done faster, smoother, and with less frustration. And sometimes, the best connection isn't always the one with the biggest numbers on paper.
Think of Ethernet as the dependable workhorse — always there, always (relatively) consistent. WiFi 7, on the other hand, is the flashy sports car, promising incredible speeds, but perhaps not always delivering in real-world traffic. We're going to see what makes each tick, and where their strengths really lie.
1. Understanding the Speed Claims
Alright, let's talk numbers! WiFi 7 boasts some pretty impressive theoretical speeds. We're talking about numbers that can reach over 40 Gbps (Gigabits per second). Yes, you read that right. It sounds insane, doesn't it? That's like downloading an entire movie library in the blink of an eye (theoretically, of course!).
Ethernet, traditionally, has had its own speed benchmarks. Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) has been the standard for quite some time. However, newer standards like 2.5 Gbps, 5 Gbps, and even 10 Gbps Ethernet are becoming increasingly common, especially in homes and offices that need to move large amounts of data. So, Ethernet is no slouch either.
Now, heres the kicker: those theoretical speeds are just that — theoretical. They represent the maximum possible speed under ideal conditions. In the real world, youre never going to see those numbers. Think of it like the MPG on a car sticker. It's a great guideline, but it rarely matches what you actually get when you're stuck in rush hour traffic.
Think of it this way: both Ethernet and WiFi speeds are like highways. The number of lanes (bandwidth) determines the theoretical maximum speed, but the actual speed depends on how congested the highway is (interference and other devices) and how fast your car (your device) can actually go.
Vs WiFi Which One Offers Faster Connections For
Real-World Performance
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks. Forget the marketing hype and laboratory tests. What kind of speeds can you actually expect in your everyday life?
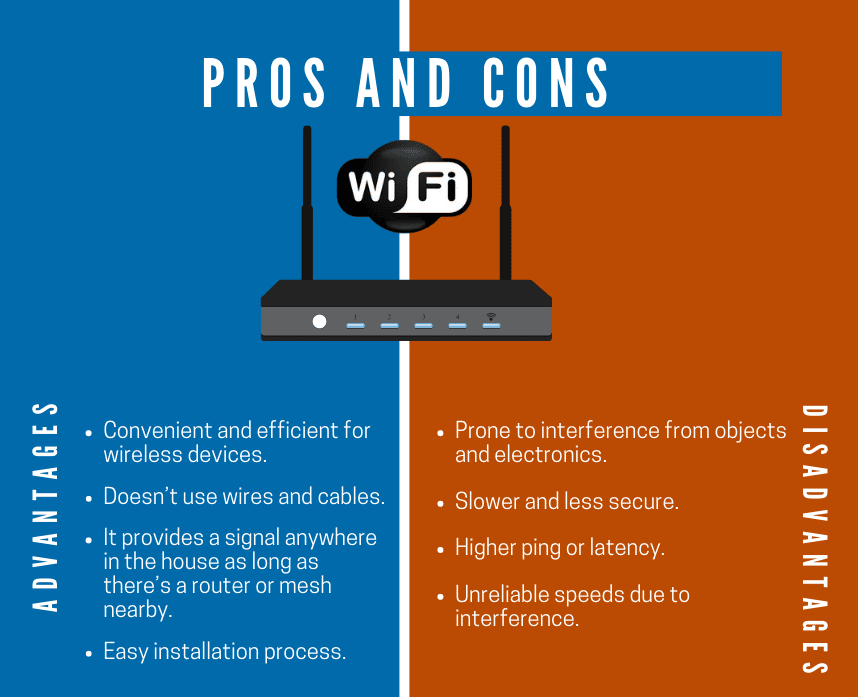
With WiFi 7, the actual speed you experience will depend on a whole host of factors, including the router you're using, the device you're connecting with (does your phone even support WiFi 7?), the distance from the router, and the amount of interference from other devices and networks. Walls, microwave ovens, nosy neighbors with their own WiFi networks — all of these can impact your speed.
Ethernet, on the other hand, is generally more consistent. You plug in, and you get pretty close to the advertised speed of your Ethernet connection (assuming your devices and cables support it). There's less interference to worry about, and the connection is typically more stable.
So, in a real-world scenario, a high-end WiFi 7 setup might outperform Gigabit Ethernet, especially if you're close to the router and there's minimal interference. However, for most people, a wired Ethernet connection will provide a more reliable and consistent experience, even if the theoretical speed is lower. Remember, consistency trumps speed, especially when you are streaming that very important, must-see video!
2. The Interference Factor
We've touched on interference, but it's worth digging into a bit more. WiFi operates on radio waves, which are susceptible to interference from all sorts of things. Your microwave oven, your Bluetooth speakers, your neighbor's WiFi network — they all compete for the same airspace. WiFi 7 aims to mitigate some of these issues with new technologies like MLO (Multi-Link Operation) and 4096-QAM, but interference will always be a factor.
MLO is like having multiple lanes on a highway for your data, allowing it to switch to less congested bands. 4096-QAM is like packing more information into each "packet" of data, increasing the overall efficiency. But even with these improvements, WiFi will always be subject to the limitations of the radio spectrum.
Ethernet, being a wired connection, is immune to most of these forms of interference. The signal travels directly from your device to the router or switch, without having to navigate a crowded airspace. This makes Ethernet a much more predictable and reliable connection for tasks that require high bandwidth and low latency, such as gaming or video conferencing.
Think of it this way: WiFi is like trying to have a conversation in a crowded room, while Ethernet is like talking on a private phone line. One is much more prone to interruptions and background noise than the other.

Which Is Faster Or Wifi
Latency
Speed isn't everything, especially when it comes to online gaming, video conferencing, or any application that requires real-time interaction. Latency, which is the delay between sending and receiving data, is just as important, if not more so.
Ethernet generally offers lower latency than WiFi. This is because the signal has a more direct and predictable path. With WiFi, the signal has to travel through the air, bounce off walls, and contend with interference, all of which can add to latency. This means faster reaction times in games, smoother video calls, and an overall more responsive experience.
WiFi 7 does aim to improve latency with features like preamble puncturing, which allows it to bypass interference more efficiently. However, even with these improvements, Ethernet will likely remain the king of low latency for the foreseeable future.
So, if you're a serious gamer or rely on real-time applications, Ethernet is still the best choice. The lower latency can make a significant difference in your performance and overall experience. Think milliseconds matter? They absolutely do!
3. The Verdict
Alright, let's wrap this up with some practical advice. When should you embrace the glorious potential of WiFi 7, and when should you stick with the tried-and-true reliability of Ethernet?
WiFi 7 is a good choice if: You need wireless connectivity, you have devices that support WiFi 7, you have a high-end WiFi 7 router, you are close to the router and there's minimal interference, and you are willing to pay a premium for the latest technology. It's also great for situations where you need flexibility and mobility.
Ethernet is the way to go if: You need a stable and reliable connection, you require low latency for gaming or other real-time applications, you want to minimize interference, you have devices that are stationary (like a desktop computer or a game console), and you want a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and circumstances. There's no one-size-fits-all answer. Consider your budget, your environment, and the types of activities you'll be using your network for. And remember, you can always use both! A combination of WiFi 7 and Ethernet can provide the best of both worlds.

Lan Vs Wifi At Victor Floyd Blog

